Java 使用 `commons-math3` 的线性和非线性拟合实例,带效果图
Java 使用 Apache commons-math 工具实现线性拟合以及非线性拟合的例子
例子查看
- GitHub
- Gitee
- 运行
src/main/java/org/wfw/chart/Main.java即可查看效果 src/main/java/org/wfw/math包下是简单的使用- 新增了 springboot web 实例,或者查看在线例子
版本说明
- JDK:1.8
- commons-math:3.6.1
一些基础知识
- 线性:两个变量之间存在一次方函数关系,就称它们之间存在线性关系。也就是如下的函数:
- 非线性:除了线性其他的都是非线性,例如:
-
矩阵:矩阵(Matrix)是一个按照长方阵列排列的复数或实数集合,可以理解为平面或者空间的坐标点。
看大佬怎么说之>>B站-线性代数的本质 - 系列合集 -
微分、积分:互为逆过程,一句话概括,微分就是求导,求某个点的极小变化量的斜率。积分是求一些列变化点的和,几何意义是面积
看大佬怎么说之>>B站-微积分的本质 - 系列合集 -
拟合:形象的说,拟合就是把平面上一系列的点,用一条光滑的曲线连接起来的过程。找到一条最符合这些散点的曲线,使得尽可能多的落在曲线上。常用的方法是
最小二乘法。也就是最小二乘问题
添加依赖
Maven 中添加依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-math3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-math3</artifactId>
<version>3.6.1</version>
</dependency>
如果你是 Gradle
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-math3
compile group: 'org.apache.commons', name: 'commons-math3', version: '3.6.1'
如何使用和验证
- 假设函数已知
- 根据函数并添加随机数
R生成一系列散点数据(蓝色) - 进行拟合,根据拟合结果生成拟合曲线
- 对比结果曲线(绿色)和散点曲线
例如:
首先根绝函数生成 取任意实数时的以及所对应的 得到数据集
然后对这组数据进行拟合,然后和已知函数 对比斜率 以及截距
1. 线性拟合
线性函数:
假设函数为:
生成数据集合:
/**
*
* y = kx + b
* f(x) = 1.5x + 0.5
*
* @return
*/
public static double[][] linearScatters() {
List<double[]> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (double x = 0; x <= 10; x += 0.1) {
double y = 1.5 * x + 0.5;
y += Math.random() * 4 - 2; // 随机数
double[] xy = {x, y};
data.add(xy);
}
return data.stream().toArray(double[][]::new);
}
进行拟合
public static Result linearFit(double[][] data) {
List<double[]> fitData = new ArrayList<>();
SimpleRegression regression = new SimpleRegression();
regression.addData(data); // 数据集
/*
* RegressionResults 中是拟合的结果
* 其中重要的几个参数如下:
* parameters:
* 0: b
* 1: k
* globalFitInfo
* 0: 平方误差之和, SSE
* 1: 平方和, SST
* 2: R 平方, RSQ
* 3: 均方误差, MSE
* 4: 调整后的 R 平方, adjRSQ
*
* */
RegressionResults results = regression.regress();
double b = results.getParameterEstimate(0);
double k = results.getParameterEstimate(1);
double r2 = results.getRSquared();
// 重新计算生成拟合曲线
for (double[] datum : data) {
double[] xy = {datum[0], k * datum[0] + b};
fitData.add(xy);
}
StringBuilder func = new StringBuilder();
func.append("f(x) =");
func.append(b >= 0 ? " " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(b));
func.append(k > 0 ? " + " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(k));
func.append("x");
return new Result(fitData.stream().toArray(double[][]::new), func.toString());
}
拟合效果
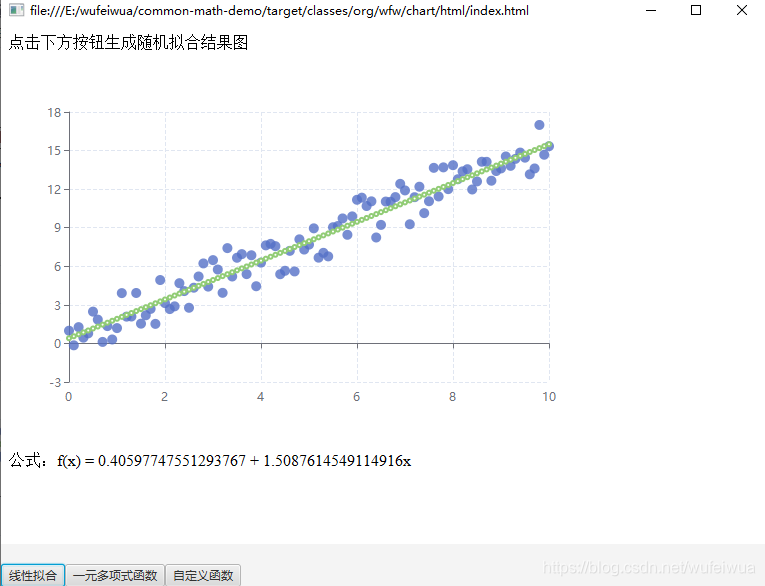
线性拟合比较简单,主要是 SimpleRegression 类的 regress() 方法,默认使用 最小二乘法优化器
2. 非线性(曲线)拟合(一元多项式)
非线性函数
假设函数为
生成数据集合:
/**
*
* f(x) = 1 + 2x + 3x^2
*
* @return
*/
public static double[][] curveScatters() {
List<double[]> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (double x = 0; x <= 20; x += 1) {
double y = 1 + 2 * x + 3 * x * x;
y += Math.random() * 60 - 10; // 随机数
double[] xy = {x, y};
data.add(xy);
}
return data.stream().toArray(double[][]::new);
}
进行拟合
public static Result curveFit(double[][] data) {
ParametricUnivariateFunction function = new PolynomialFunction.Parametric();/*多项式函数*/
double[] guess = {1, 2, 3}; /*猜测值 依次为 常数项、1次项、二次项*/
// 初始化拟合
SimpleCurveFitter curveFitter = SimpleCurveFitter.create(function,guess);
// 添加数据点
WeightedObservedPoints observedPoints = new WeightedObservedPoints();
for (double[] point : data) {
observedPoints.add(point[0], point[1]);
}
/*
* best 为拟合结果
* 依次为 常数项、1次项、二次项
* 对应 y = a + bx + cx^2 中的 a, b, c
* */
double[] best = curveFitter.fit(observedPoints.toList());
/*
* 根据拟合结果重新计算
* */
List<double[]> fitData = new ArrayList<>();
for (double[] datum : data) {
double x = datum[0];
double y = best[0] + best[1] * x + best[2] * x * x; // y = a + bx + cx^2
double[] xy = {x, y};
fitData.add(xy);
}
StringBuilder func = new StringBuilder();
func.append("f(x) =");
func.append(best[0] > 0 ? " " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(best[0]));
func.append(best[1] > 0 ? " + " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(best[1]));
func.append("x");
func.append(best[2] > 0 ? " + " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(best[2]));
func.append("x^2");
return new Result(fitData.stream().toArray(double[][]::new), func.toString());
}
拟合效果
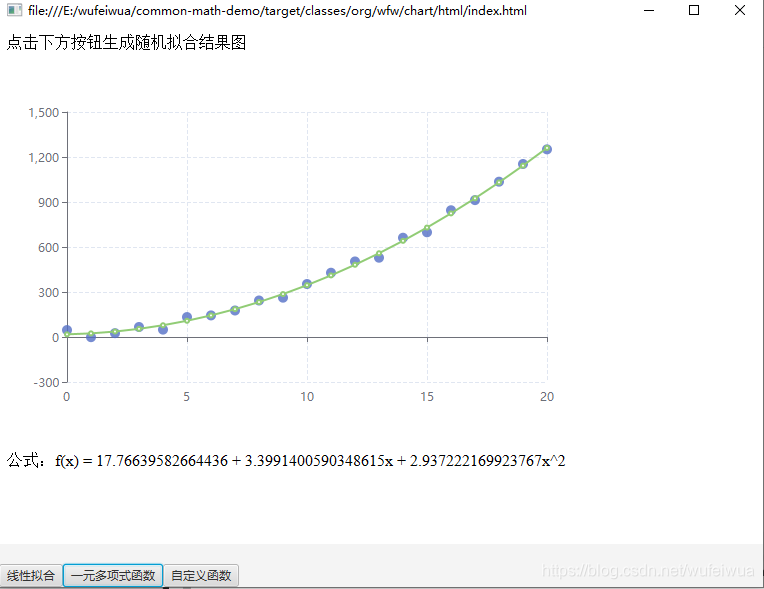
一元多项式曲线的拟合多了一些步骤。但是总归也是不难的。主要是 SimpleCurveFitter 类以及 ParametricUnivariateFunction 接口。
3. 自定义函数拟合(一元多项式)
总得来说,貌似线性和一元多项式都不难。不过,实际工作或者学术中,一般都是自定义的函数。
假设有一元多项式函数:
需要拟合出 a,b,c,d 四个参数的值。
方法:
- 实现
ParametricUnivariateFunction接口 - 自定义函数,实现
value方法 - 解偏微分方程,实现
gradient方法 - 设置需要拟合的点
- 调用
SimpleCurveFitter#fit方法进行拟合
不着急写代码,先看ParametricUnivariateFunction 这个接口的源码:
/**
* An interface representing a real function that depends on one independent
* variable plus some extra parameters.
*
* @since 3.0
*/
public interface ParametricUnivariateFunction {
/**
* Compute the value of the function.
* 计算函数的值
* @param x Point for which the function value should be computed.
* @param parameters Function parameters.
* @return the value.
*/
double value(double x, double ... parameters);
/**
* Compute the gradient of the function with respect to its parameters.
* 计算函数相对于某个参数的导数
* @param x Point for which the function value should be computed.
* @param parameters Function parameters.
* @return the value.
*/
double[] gradient(double x, double ... parameters);
}
value方法很简单,就是说计算函数 的值。说人话就是自定义函数的gradient方法为返回一个数组,其实意思就是求偏微分方程,对每一个要拟合的参数求导就行
不会偏微分方程? 点这里
按格式输入你的方程=>输入自变量=>输入求导阶数(一般都是 1 阶)=>计算
好了开始写代码吧,假设函数如下:
- 自定义
MyFunction实现ParametricUnivariateFunction接口:
static class MyFunction implements ParametricUnivariateFunction {
public double value(double x, double ... parameters) {
double a = parameters[0];
double b = parameters[1];
double c = parameters[2];
double d = parameters[3];
return d + ((a - d) / (1 + Math.pow(x / c, b)));
}
public double[] gradient(double x, double ... parameters) {
double a = parameters[0];
double b = parameters[1];
double c = parameters[2];
double d = parameters[3];
double[] gradients = new double[4];
double den = 1 + Math.pow(x / c, b);
gradients[0] = 1 / den; // 对 a 求导
gradients[1] = -((a - d) * Math.pow(x / c, b) * Math.log(x / c)) / (den * den); // 对 b 求导
gradients[2] = (b * Math.pow(x / c, b - 1) * (x / (c * c)) * (a - d)) / (den * den); // 对 c 求导
gradients[3] = 1 - (1 / den); // 对 d 求导
return gradients;
}
}
生成数据散点
/**
*
* <pre>
* f(x) = d + ((a - d) / (1 + Math.pow(x / c, b)))
* a = 1500
* b = 0.95
* c = 65
* d = 35000
* </pre>
*
* @return
*/
public static double[][] customizeFuncScatters() {
MyFunction function = new MyFunction();
List<double[]> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (double x = 7; x <= 10000; x *= 1.5) {
double y = function.value(x, 1500, 0.95, 65, 35000);
y += Math.random() * 5000 - 2000; // 随机数
double[] xy = {x, y};
data.add(xy);
}
return data.stream().toArray(double[][]::new);
}
拟合自定义函数
public static Result customizeFuncFit(double[][] scatters) {
ParametricUnivariateFunction function = new MyFunction();/*多项式函数*/
double[] guess = {1500, 0.95, 65, 35000}; /*猜测值 依次为 a b c d 。必须和 gradient 方法返回数组对应。如果不知道都设置为 1*/
// 初始化拟合
SimpleCurveFitter curveFitter = SimpleCurveFitter.create(function,guess);
// 添加数据点
WeightedObservedPoints observedPoints = new WeightedObservedPoints();
for (double[] point : scatters) {
observedPoints.add(point[0], point[1]);
}
/*
* best 为拟合结果 对应 a b c d
* 可能会出现无法拟合的情况
* 需要合理设置初始值
* */
double[] best = curveFitter.fit(observedPoints.toList());
double a = best[0];
double b = best[1];
double c = best[2];
double d = best[3];
// 根据拟合结果生成拟合曲线散点
List<double[]> fitData = new ArrayList<>();
for (double[] datum : scatters) {
double x = datum[0];
double y = function.value(x, a, b, c, d);
double[] xy = {x, y};
fitData.add(xy);
}
// f(x) = d + ((a - d) / (1 + Math.pow(x / c, b)))
StringBuilder func = new StringBuilder();
func.append("f(x) =");
func.append(d > 0 ? " " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(d));
func.append(" ((");
func.append(a > 0 ? "" : "-");
func.append(Math.abs(a));
func.append(d > 0 ? " - " : " + ");
func.append(Math.abs(d));
func.append(" / (1 + ");
func.append("(x / ");
func.append(c > 0 ? "" : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(c));
func.append(") ^ ");
func.append(b > 0 ? " " : " - ");
func.append(Math.abs(b));
return new Result(fitData.stream().toArray(double[][]::new), func.toString());
}
拟合效果
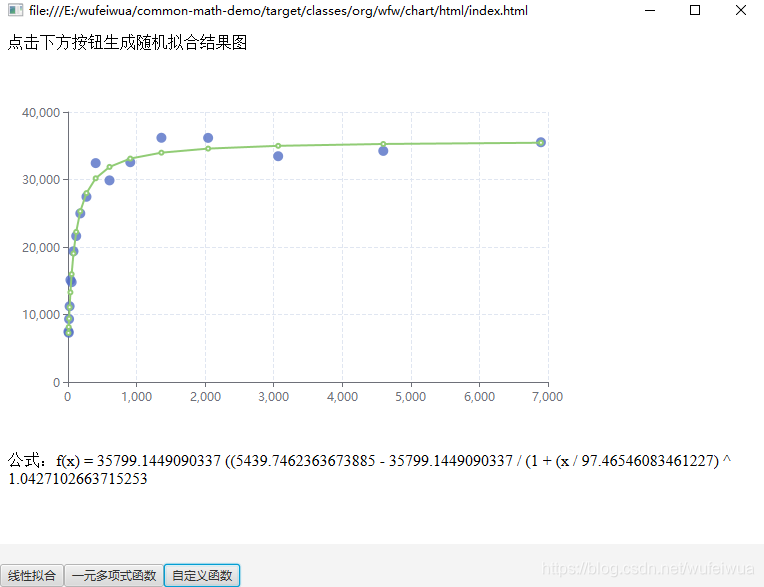
4. 多元多项式拟合
我用的 javafx8 版本不支持 WebGL 所以无法通过按钮直接直观展示拟合效果。我用拟合前得数据和拟合后重新计算的数据进行对比
方程
4.1 构造数据
假设: ,则函数 为
根据这个函数构造数据
/**
* 生成随机数
*/
public static double[][] randomX() {
List<double[]> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (double i = 0; i < 10; i += 0.1) {
double x1 = Math.cos(i);
double x2 = Math.sin(i);
data.add(new double[]{x1, x2});
}
return data.stream().toArray(double[][]::new);
}
/**
* f(x1,x2) = y = a + b * x1 + c * sin(x2)
* @param arr
* @return
*/
public static double[] randomY(double[][] arr) {
if (arr != null && arr.length > 0) {
int len = arr.length;
double[] y = new double[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// f(x1,x2) = y = 20 + x1 + 12 * sin(x2)
double[] x = arr[i];
// 构造数据
y[i] = functionConstructorY(x);
}
return y;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 已知的函数为: f(x1,x2) = y = 20 + 2 * x1 + 12 * sin(x2)
* 即:f(x1,x2) = y = a + b * x1 + c * sin(x2) 中
* a = 20, b = 2, c = 12
* @param x
* @return
*/
public static double functionConstructorY(double[] x) {
double x1 = x[0], x2 = x[1];
return 20 + 2 * x1 + Math.sin(10 * x2);
}
4.2 拟合
多元多项式的拟合主要用到 MultipleLinearRegression 接口,它有三个实现方式。我们选择最小二乘法的实现 OLSMultipleLinearRegression
/**
* 多元多项式数据
* 已知: f(x1,x2) = y = a + b * x1 + c * sin(x2)
*
*/
public static double[][] multiVarPolyScatters() {
double[][] x = randomX();
double[] y = randomY(x);
OLSMultipleLinearRegression ols = new OLSMultipleLinearRegression();
ols.newSampleData(y, x);
// ct 拟合的常数项(系数)。对应 a,b,c
double[] ct = ols.estimateRegressionParameters();
}
4.3 验证
根据上面的拟合结果重新计算 的值
/**
* f(x1,x2) = y = a + b * x1 + c * sin(x2)
* @param ct 拟合的常数项(系数)。对应 a,b,c
* @param x x 的值。对应 x1,x2
* @return
*/
public static double functionValueY(double[] ct, double[] x) {
double a = ct[0], b = ct[1], c = ct[2];
double x1 = x[0], x2 = x[1];
return a + b * x1 + Math.sin(c * x2);
}
/**
* 多元多项式数据
* 已知: f(x1,x2) = y = a + b * x1 + c * sin(x2)
* @return
* arr[0] 对应所有的 y 的值
* arr[1] 对应所有的 x1 的值
* arr[2] 对应所有的 x2 的值
*/
public static double[][] multiVarPolyScatters() {
double[][] x = randomX();
double[] y = randomY(x);
OLSMultipleLinearRegression ols = new OLSMultipleLinearRegression();
ols.newSampleData(y, x);
// ct 即为拟合结果
double[] ct = ols.estimateRegressionParameters();
double[] valueY = new double[x.length];
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
// 重新计算 y 的值。与原有构造的 y 对比
valueY[i] = functionValueY(ct, x[i]);
}
// 散点数据用于 Echarts 画图
double[][] data = new double[x.length][3];// x1, x2, y
for (int i = 0; i < valueY.length; i++) {
// ==================== x1 ====== x2 ======= y ====
data[i] = new double[]{x[i][0], x[i][1], valueY[i]};
}
return data;
}
4.4 画图
Echarts 3D画图的工具在 https://echarts.apache.org/examples/zh/editor.html?c=line3d-orthographic&gl=1 这个地方。我们将构造数据的函数改为我们的
// ...
var data = [];
// Parametric curve
for (var t = 0; t < 10; t += 0.1) {
// 这里改成我们的函数。其他的都不变
var x = Math.cos(t);
var y = Math.sin(t);
var z = 20 + 2 * x + 12 * Math.sin(y);
data.push([x, y, z]);
}
// ...
那可以得到这样一张图

然后我们运行 org.wfw.chart.data.MultipleLinearRegressionData#main() 方法后将得到的数据整个赋值给 data 覆盖也行。我们就得到了如下的图

拟合的结果是 $$ a = 20.01068756847646, b = 2.036022472817587, c = 10.571979017911016 $$ 和我们一开始的确定好的值也差不多
4.5 多说两句
calculateRSquared()计算calculateAdjustedRSquared()计算 ,调整后的estimateRegressionParameters()拟合常数项
关于
newSampleData()方法参数的 y 和 x 样本
/**
* Loads model x and y sample data, overriding any previous sample.
*
* Computes and caches QR decomposition of the X matrix.
* @param y the [n,1] array representing the y sample
* @param x the [n,k] array representing the x sample
* @throws MathIllegalArgumentException if the x and y array data are not
* compatible for the regression
*/
public void newSampleData(double[] y, double[][] x) throws MathIllegalArgumentException {
validateSampleData(x, y);
newYSampleData(y);
newXSampleData(x);
}
源码是这样的,y 就是 的值,而 x 中的 k 代表的是 的值,是顺序对应的